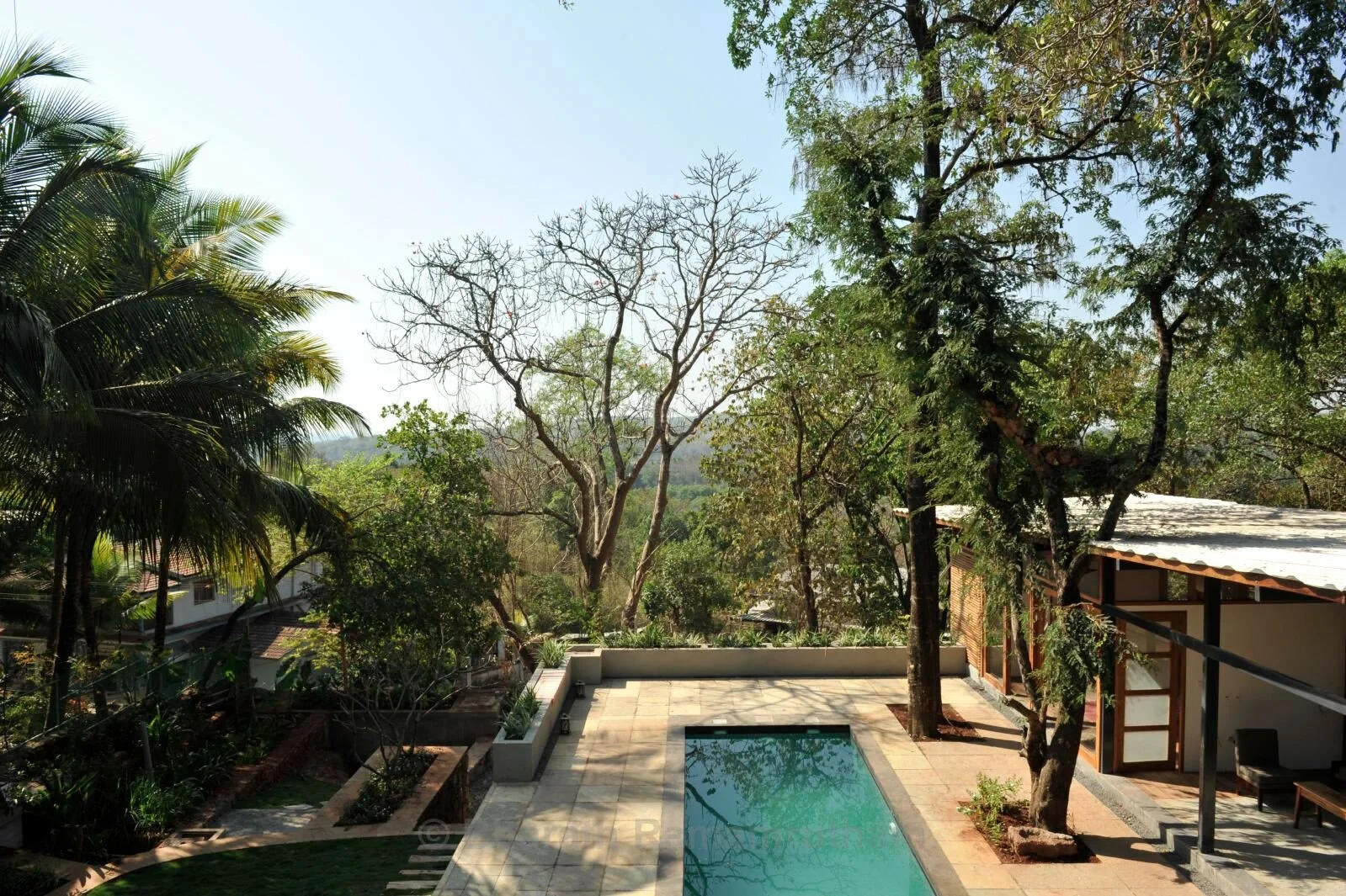
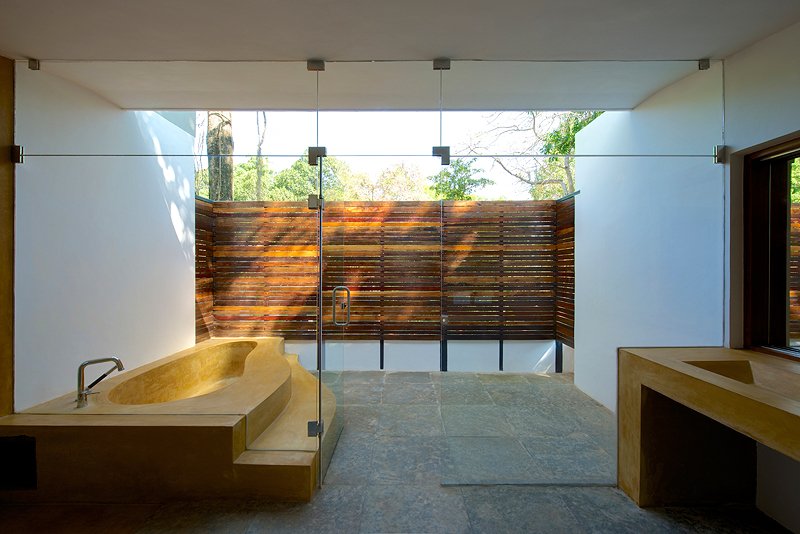
Sakshi R Ghodake
“When we reconnect with nature, we will be able to restore ourselves.”
― Lailah Gifty Akita
Kishan Bagh, Jaipur
Jaipur has been touched upon by Architect Pradip Kishan and his team to ornament the existing gift of nature which Kishan Bagh holds. He had a great vision of how the park should be designed well enough to convey the importance of restoring and conserving our ecosystem. Having worked on Rao Jodha Rock Park in Jodhpur, Pradip Kishan took on the mammoth task of restoring Kishan Bagh dunes into a natural desert landscape.
Kishan Bagh
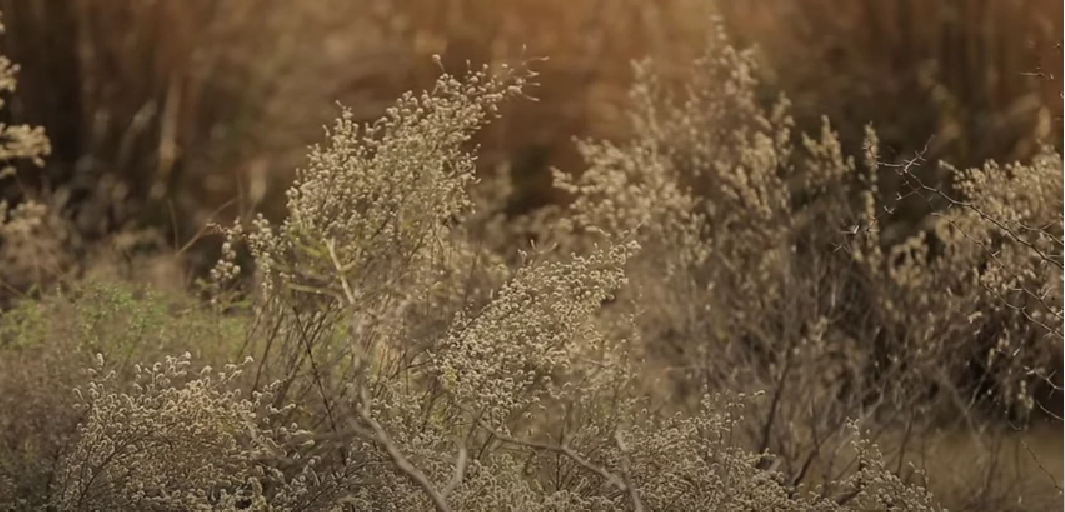
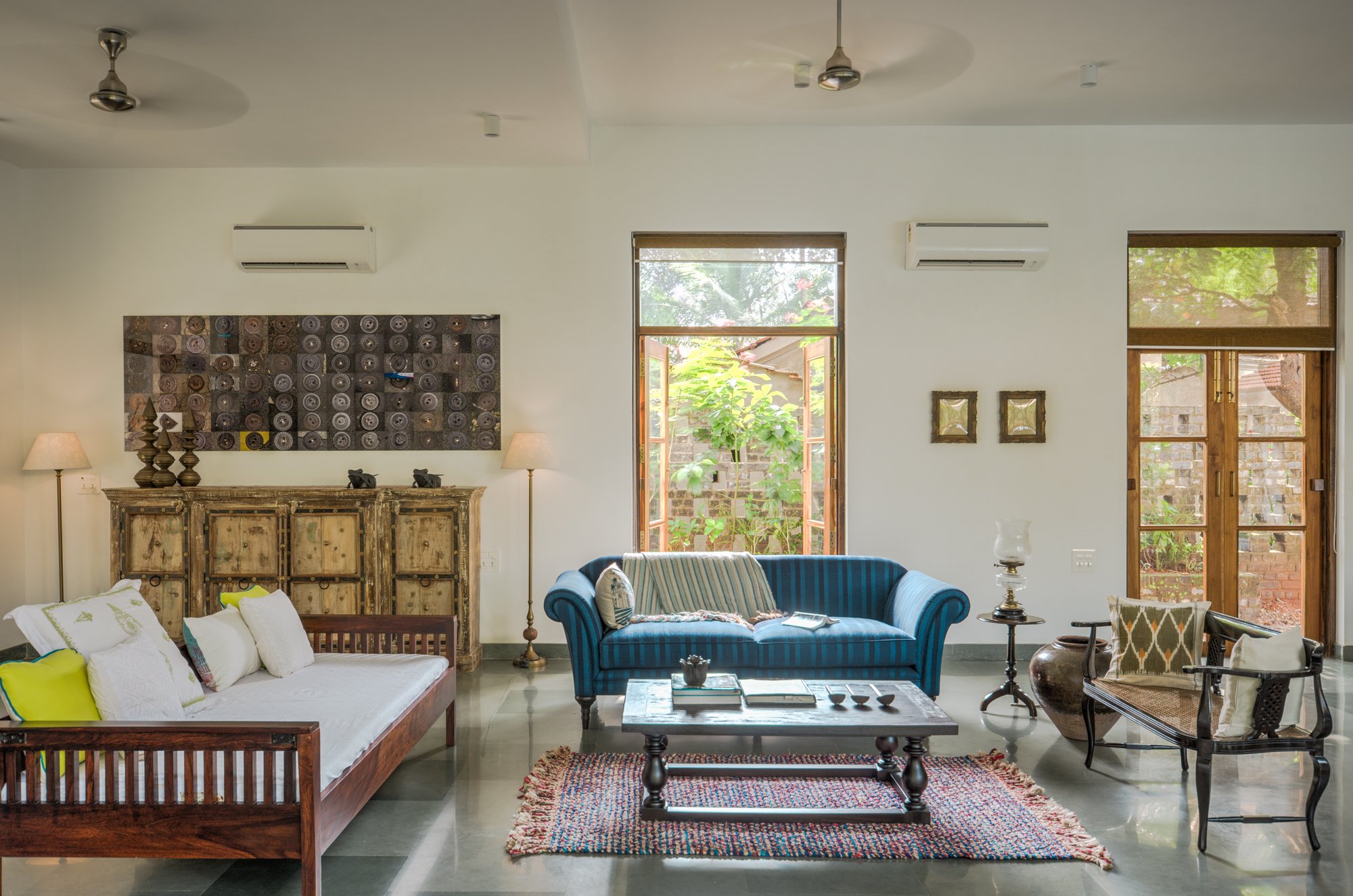
Scenic view from the park.
The design proposes restoring the vegetation of sand dunes, designing a place for people to understand the ecology and bringing the endangered plant community of the Thar to be conserved.
Heteropogon Spa (grass)
Rohida
Saccharum
Akara
Kumatha acacia sengal
Phragmites Australis
The design is influenced by the explorations of the desert landscape of western Rajasthan, called Roee by the locals, also seen in the jungles of Thar with different plant communities which have evolved in that particular changing climatic condition. Hence, native flora like Saccharum, Rohida, Kumatha acacia sengal, Akada, Dhatura, and Phragmites Australis have been planted according to the different soil textures where each contributes to the ecosystem in the desert.
Distinct color layers of sandstone due to the presence of different minerals.
Migmatites – double-cooked stones, consisting of two or more constituents often layered repetitively
According to Pradip Kishan parks have always been remembered in colonial style, while they should ideally be reminisced based on the native nature of the plants and surrounding. Parks have now become sanitized spaces and the trees which are featured are grown for their colourful blossoms which will eventually last for a certain period that add an aesthetic charm in landscape and does not talk about the habitat. This clearly says that the idea of beauty should change.
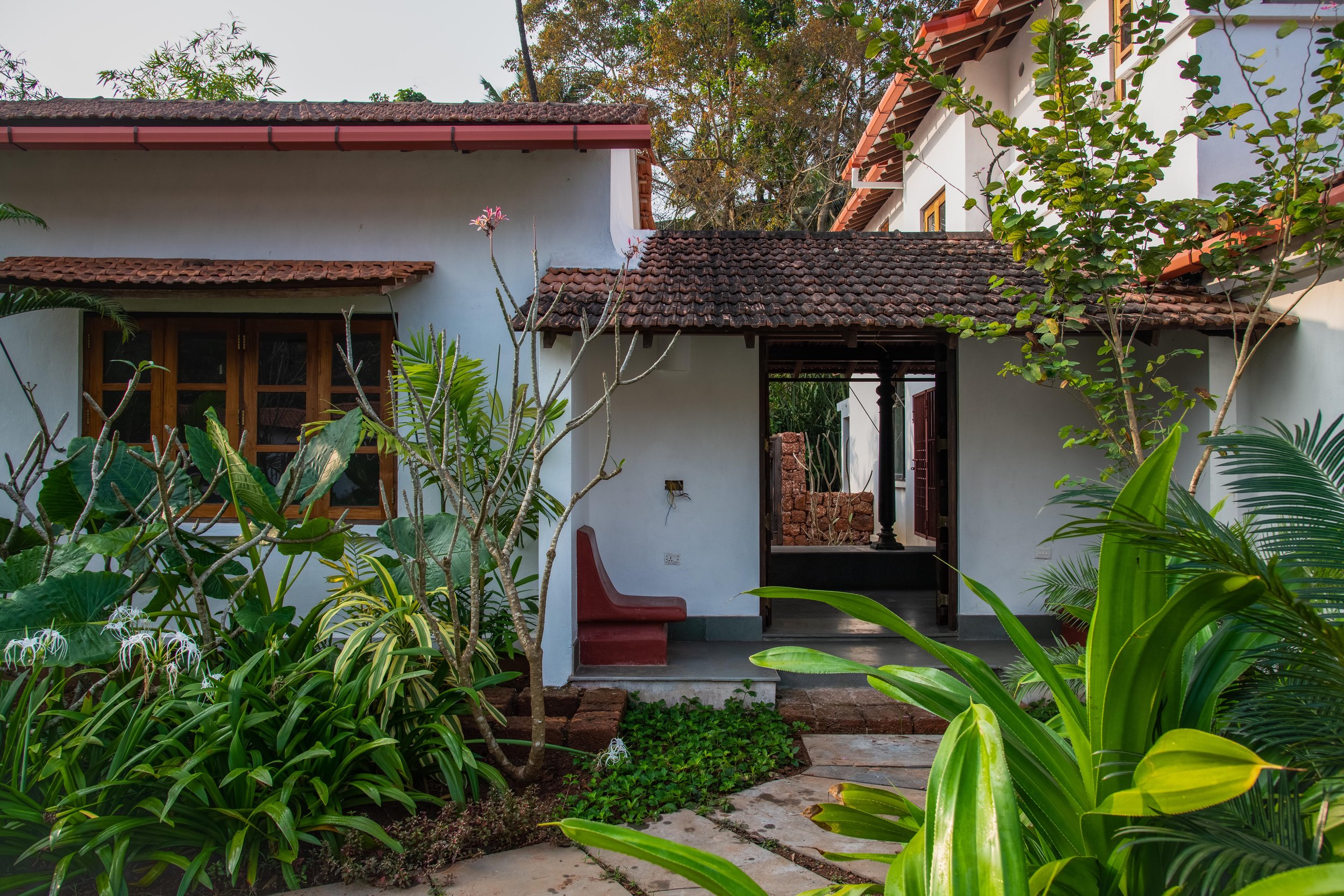
Sand dune desert park
The Grounded team had visited Rao Jodha Park in Jodhpur which is also an ecology restoration project led by Pradip Krishan. Read about it here. From this we have understood that experience stands out based on the interpretation which is based on telling the story of a landscape and the wildlife that it supports. Here at Grounded, we are making an effort to sensitize the urban and rural populations to the wild through our designs.
Watch more about Kishan Bagh, here.