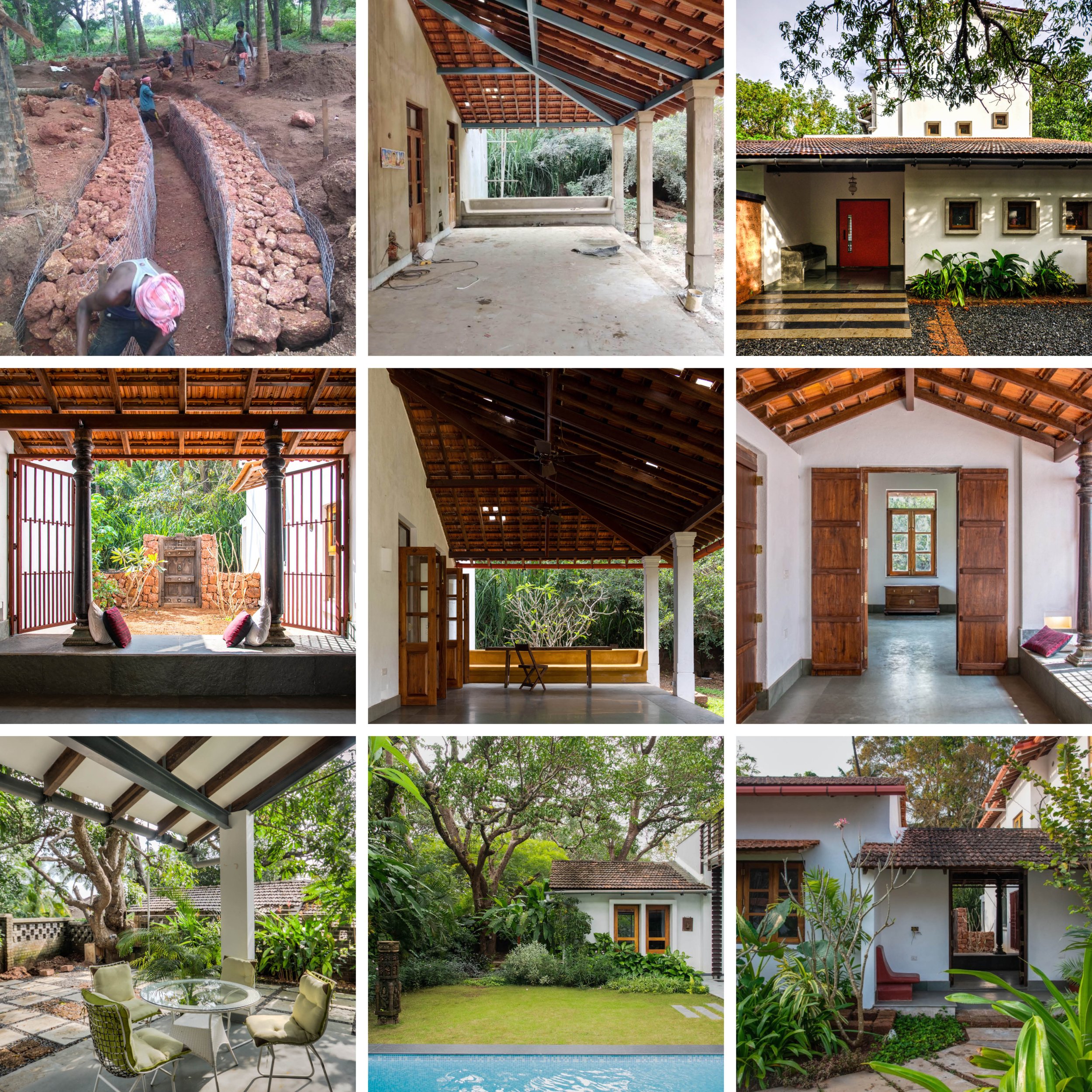
The House with Three Pavilions is a sustainable house in Goa, designed and developed by GROUNDED.
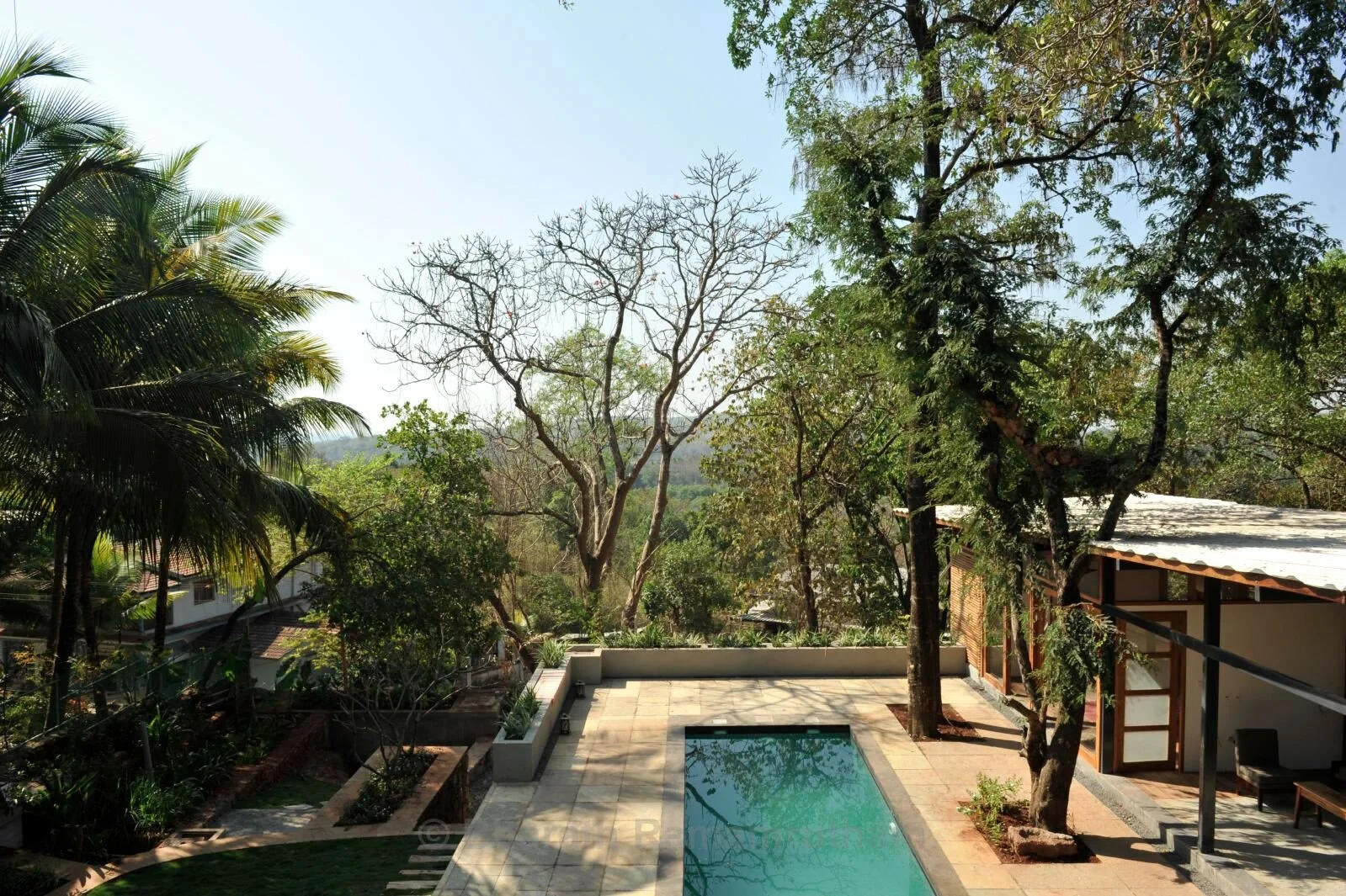
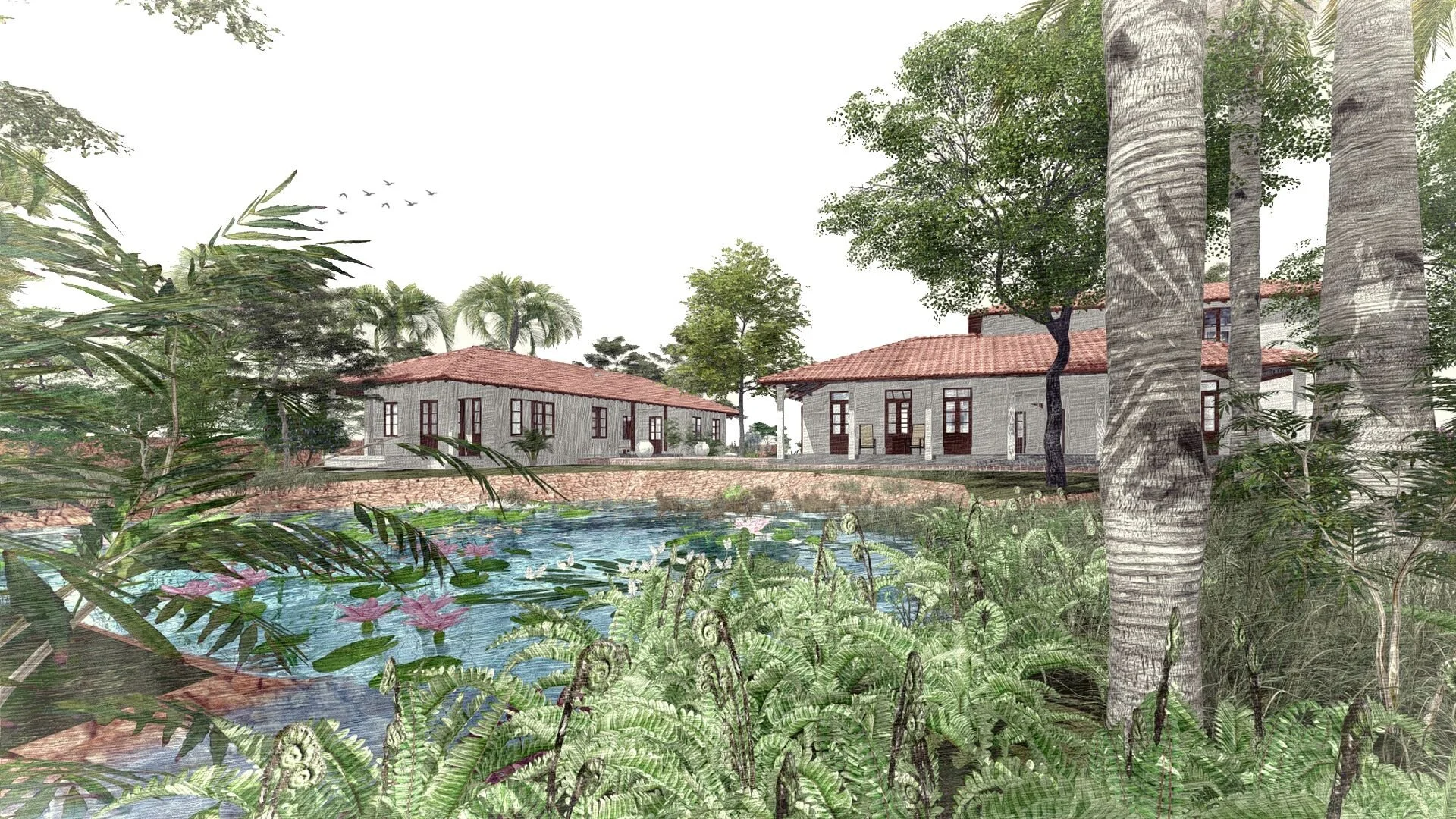
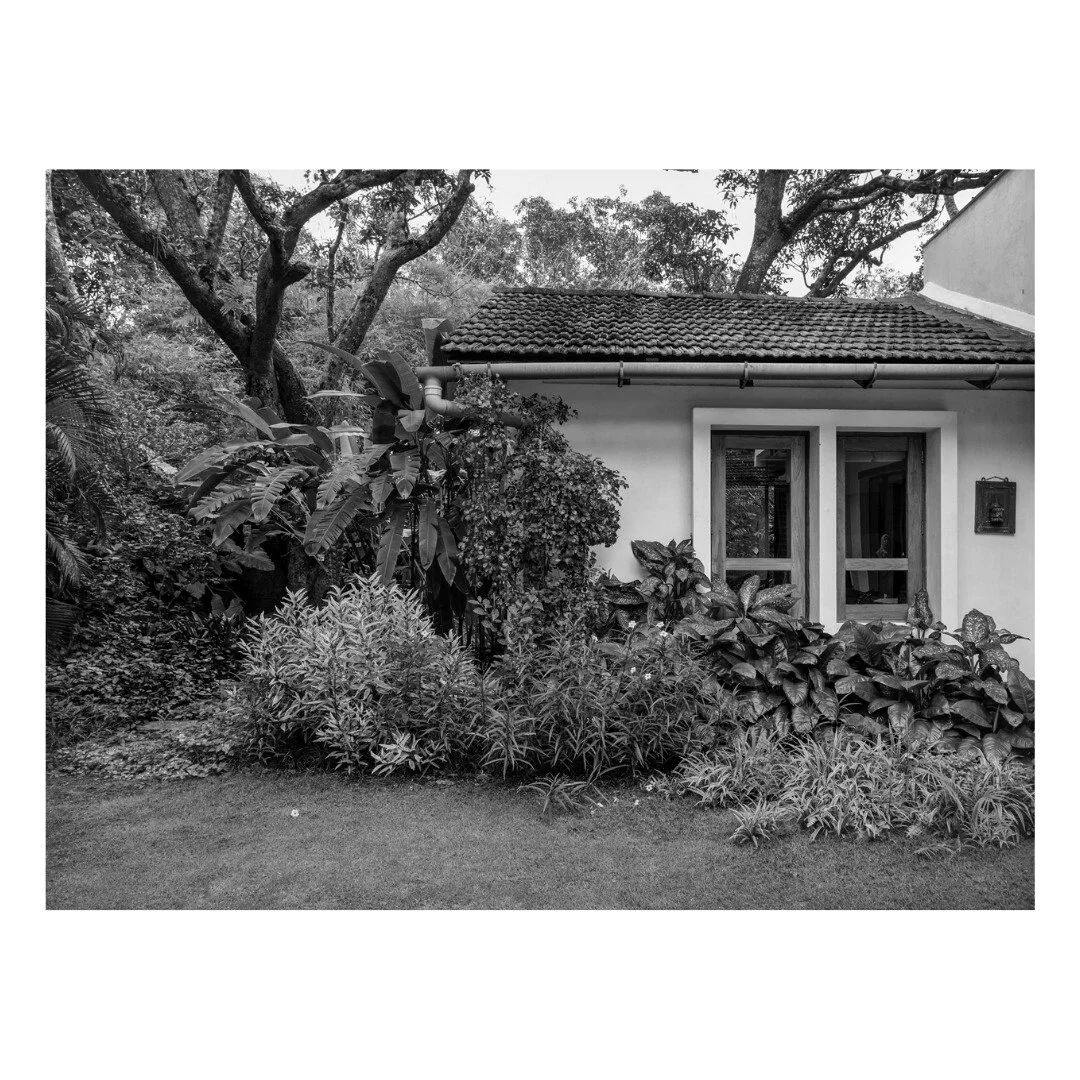
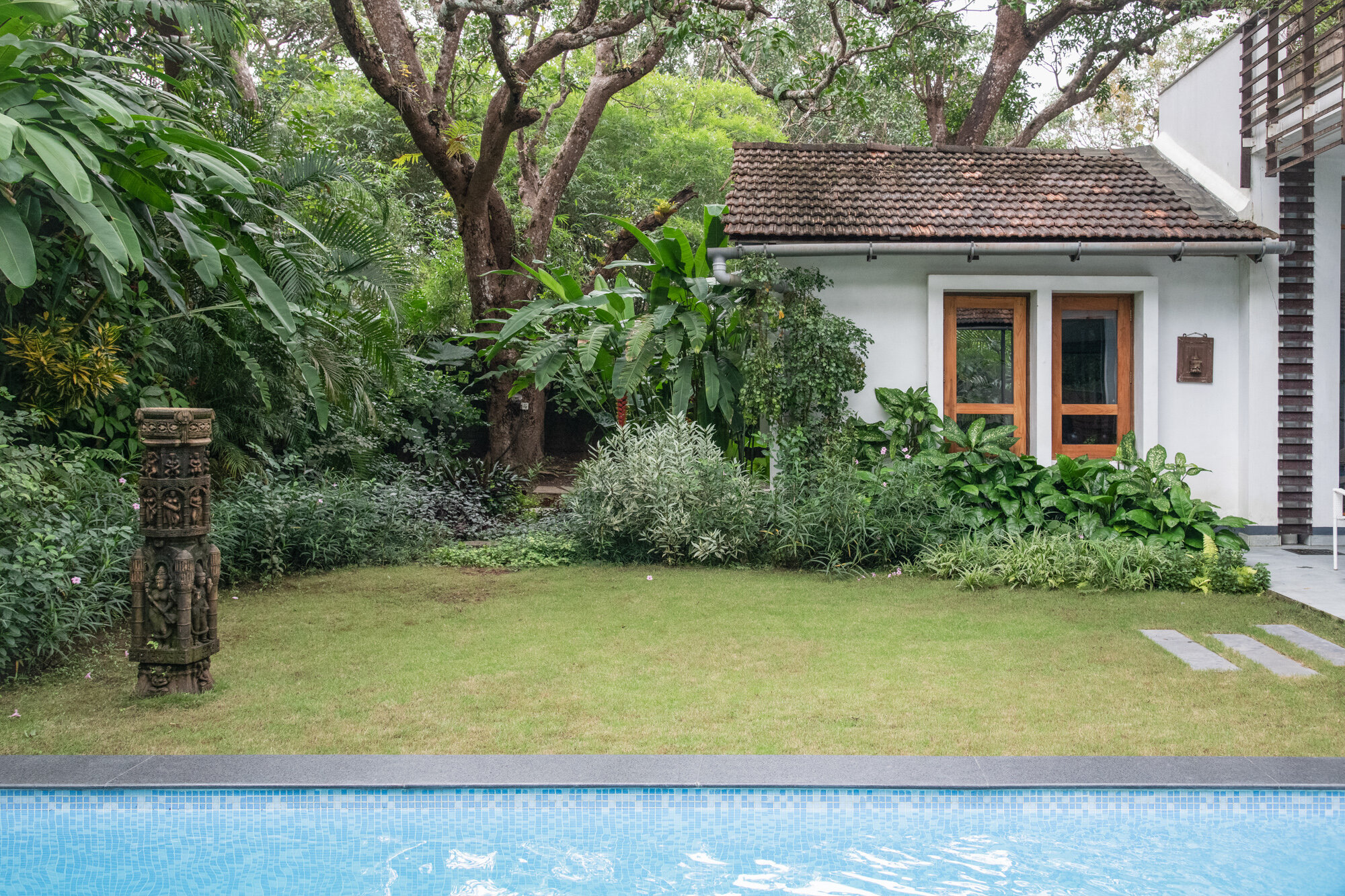
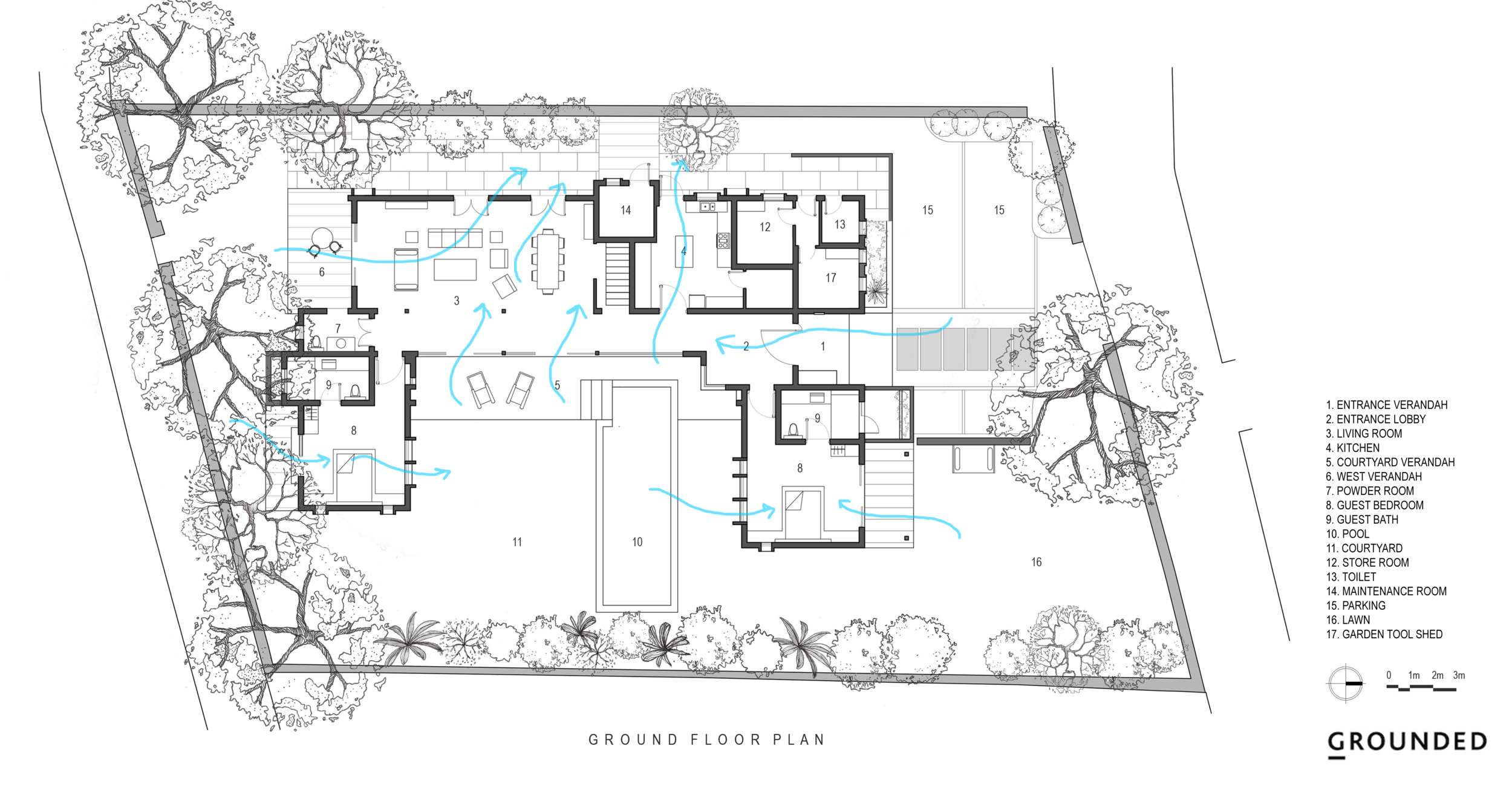
The house explores the intimate relationship between the land, its people, water, and the biodiversity that exists in Goa in India. It is designed as a cluster of three pavilions that gently weave around existing trees in an attempt to coexist with nature and to minimize the impact of new construction on virgin land.
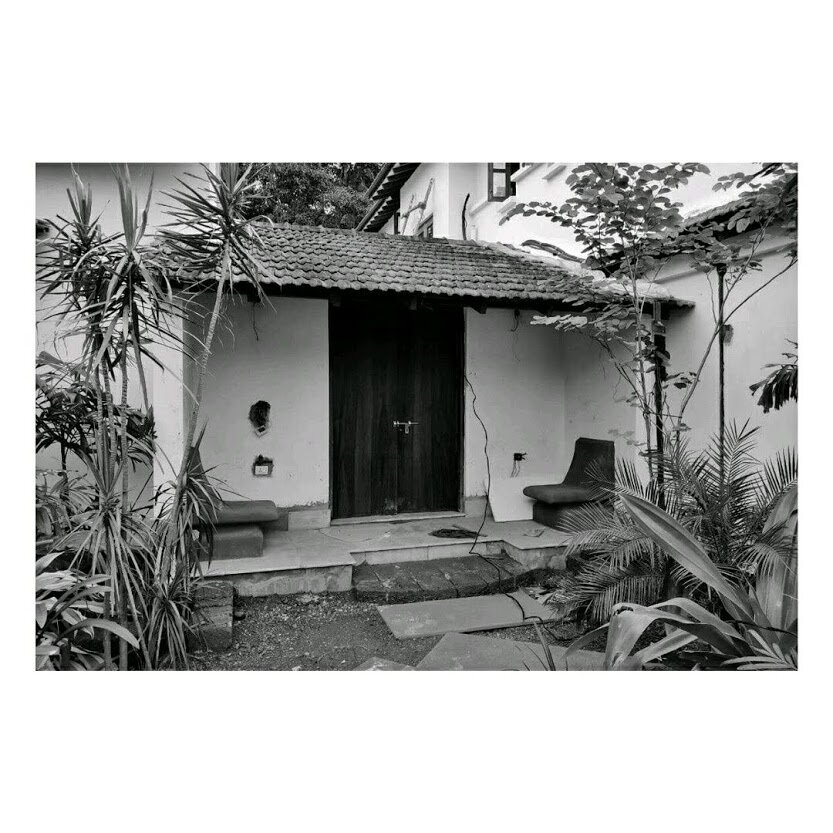
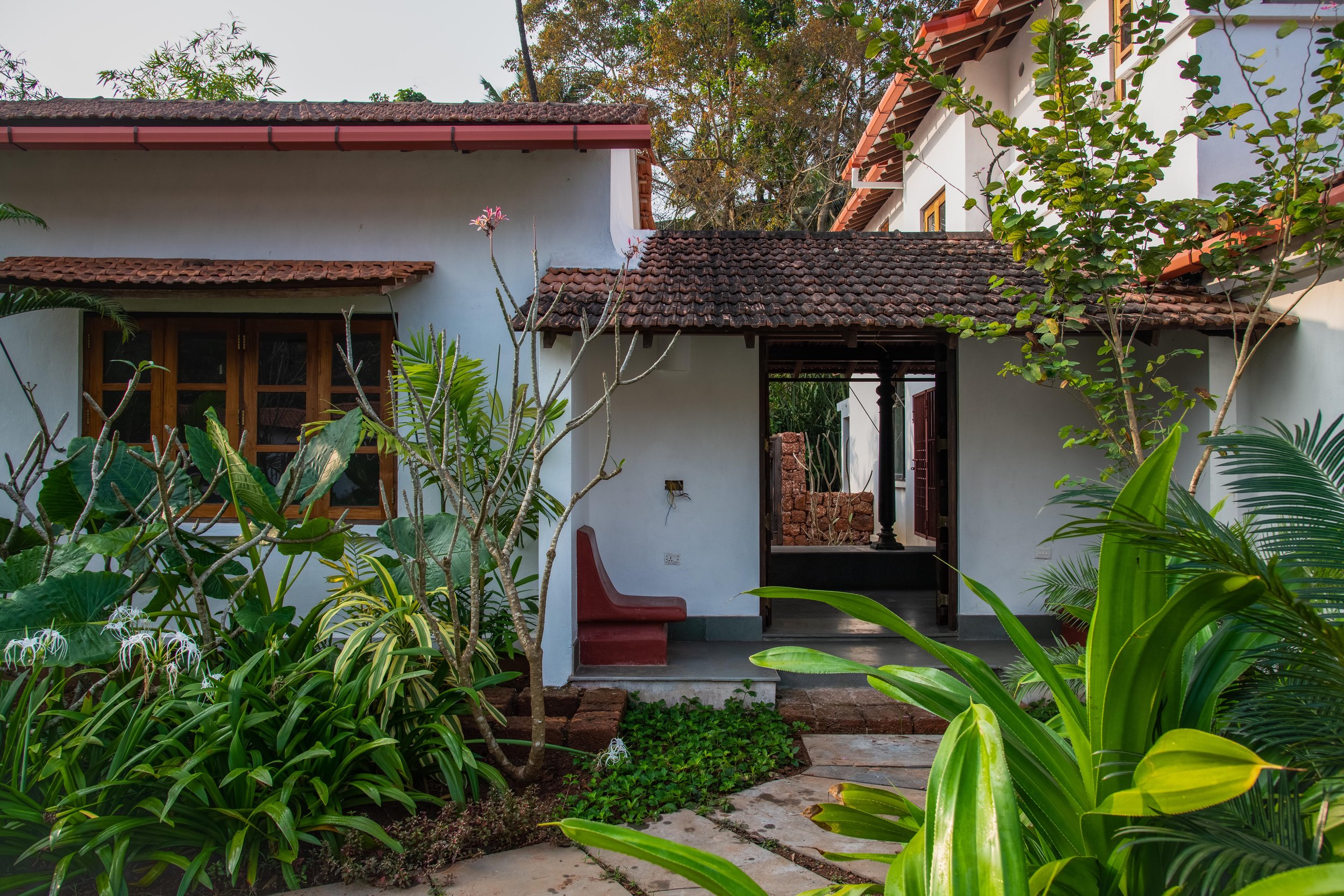
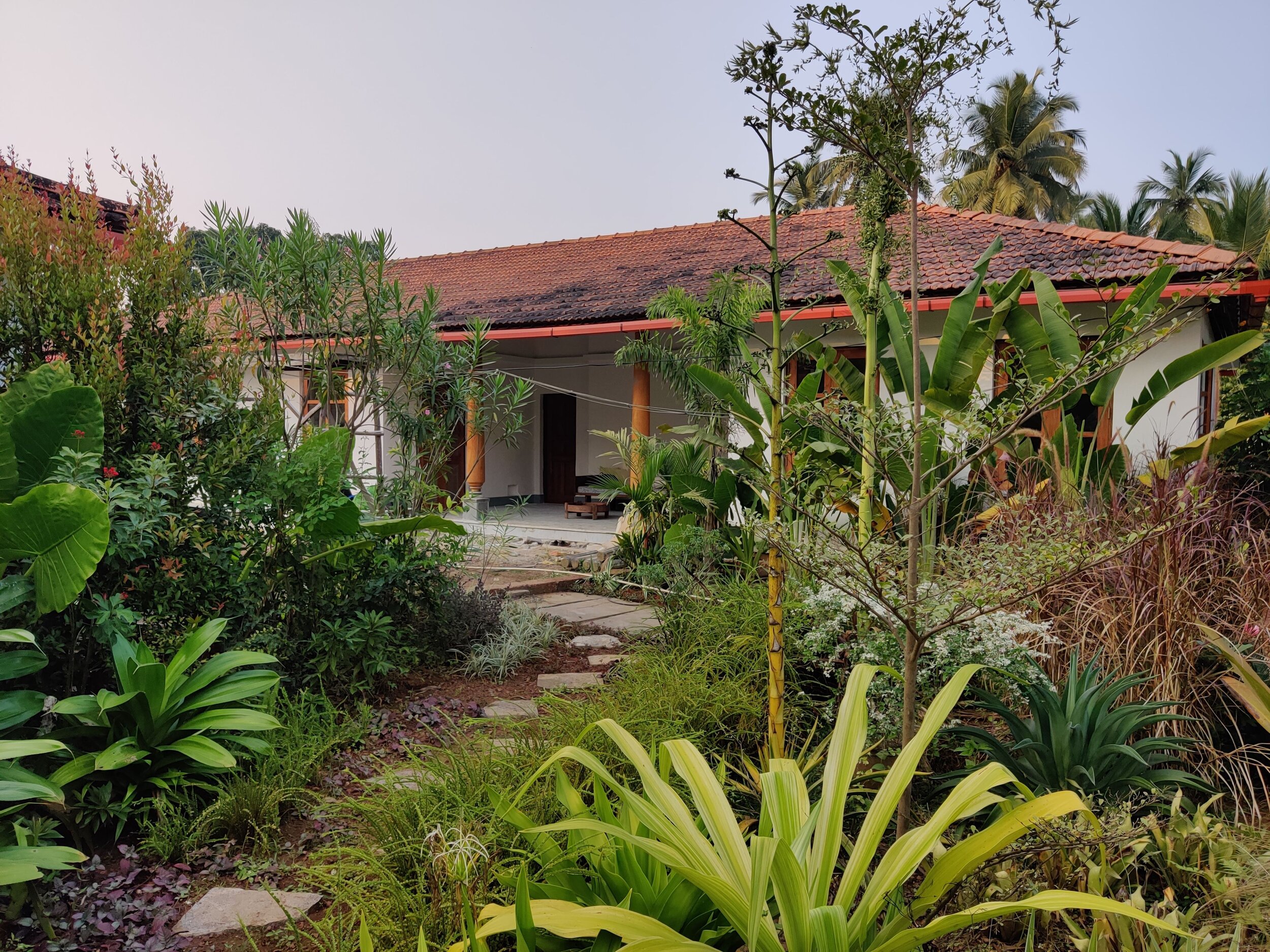
The architecture of the house takes inspiration from the surrounding Goan village houses. Mostly constructed as ground-floor structures, each pavilion attempts to match the volumetrics of its village peers. Throughout, a simple sweeping roof form is used in red terracotta tile that is ubiquitous to the Goan village built-landscape. Proportions are borrowed from doors, windows, and plaster bands of vernacular Goan structures even as a distinct contemporary style is articulated in the design.
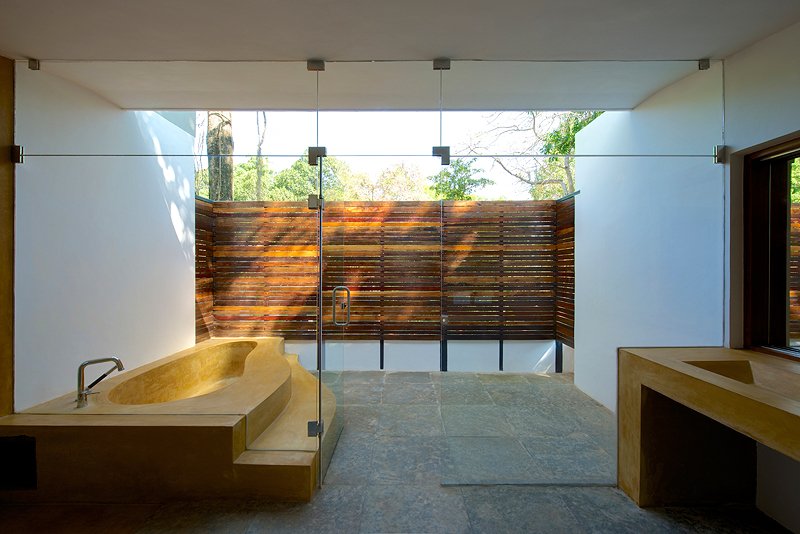
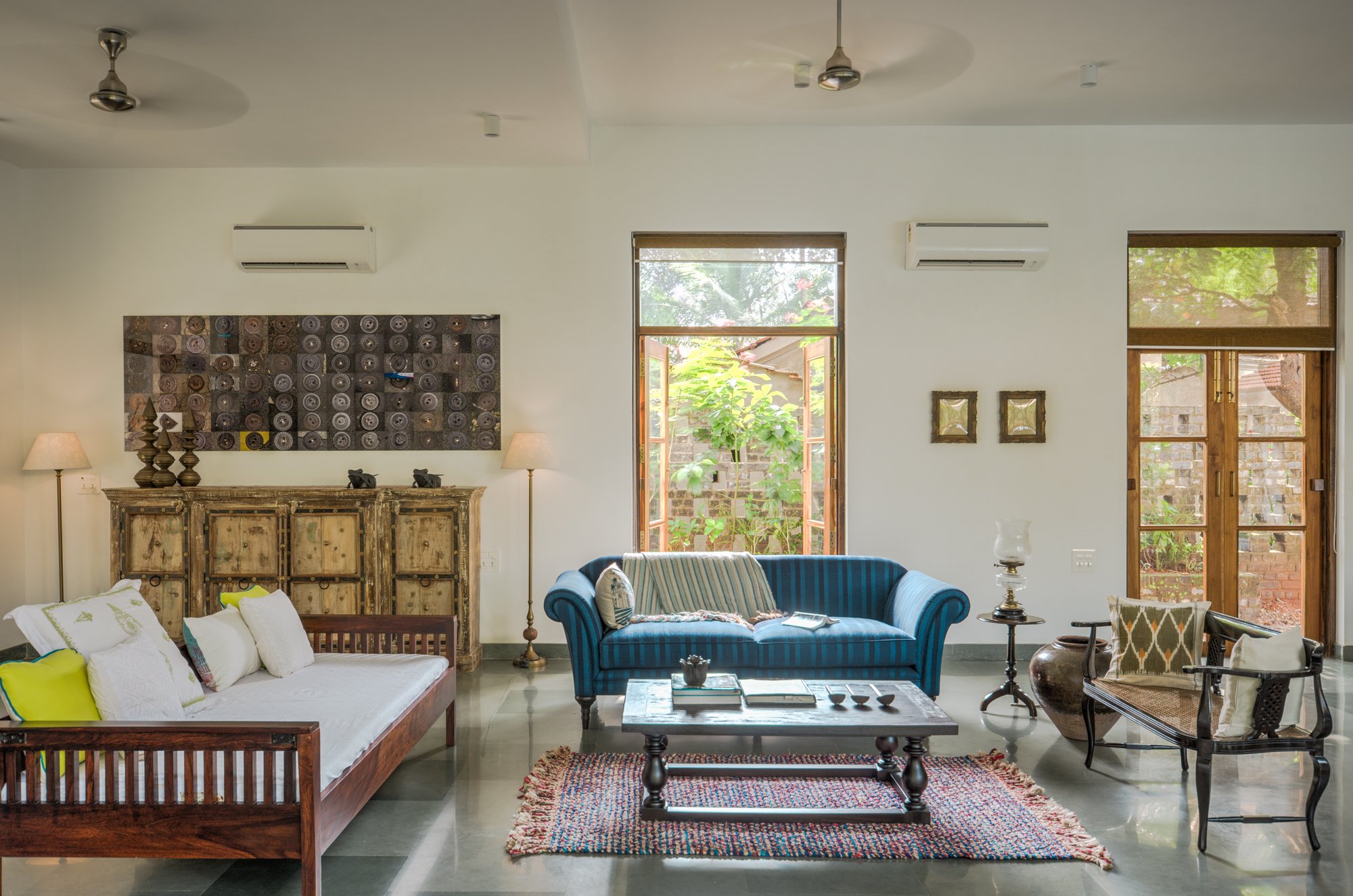
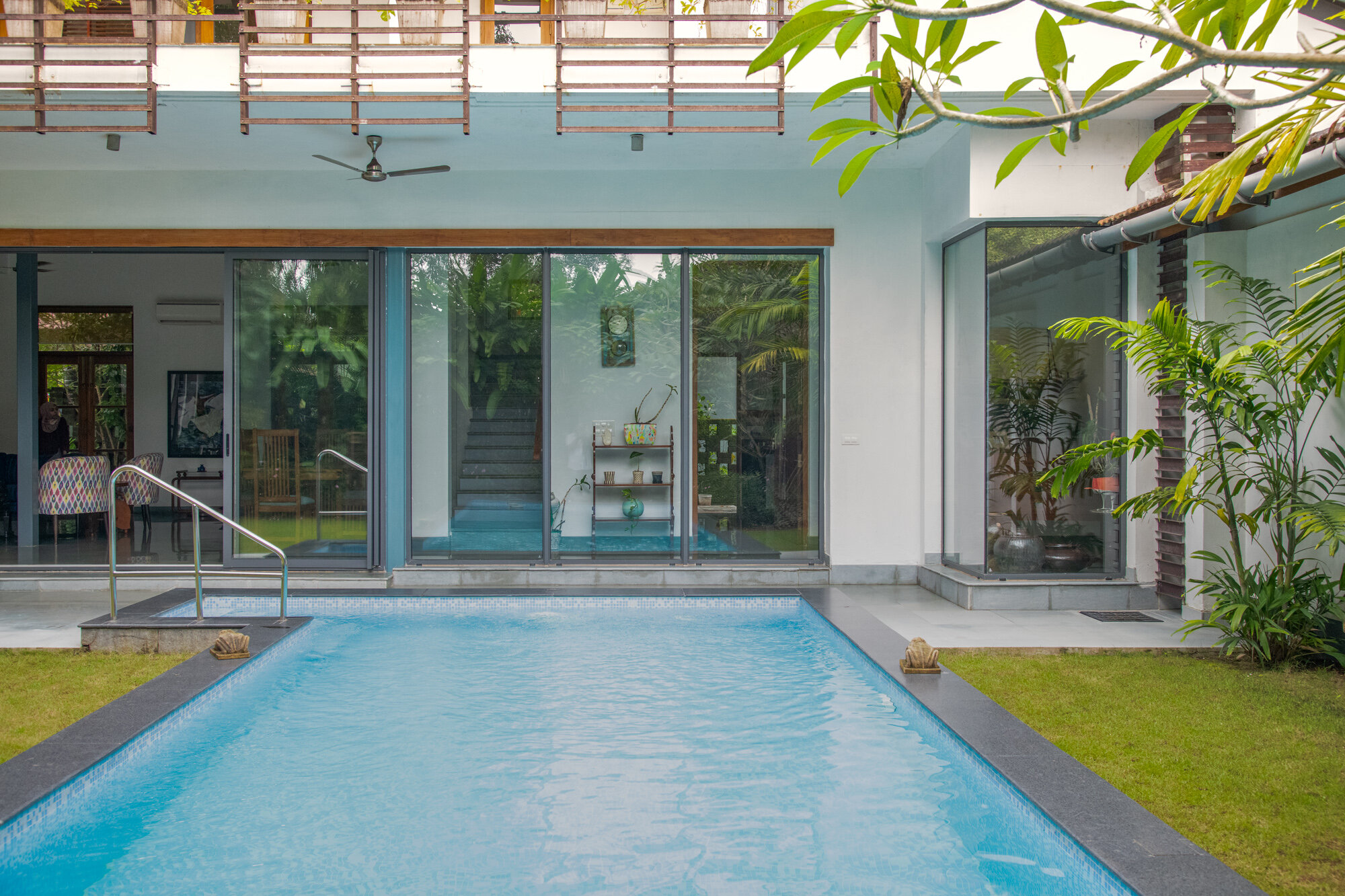
With a focus on connection with nature, the materials used in the house are kept subtle and natural. All floors are finished with a natural Indian ‘kota’ stone in a blue-green color that merges with the landscape. Pigmented cement and exposed local ‘laterite’ are used extensively to mirror the rustic countryside character. ‘Teak’ is used for doors and windows to add warmth and rich texture to the interiors. Antique wood columns and stone pedestals are also incorporated to bring a sense of luxury and timelessness throughout.
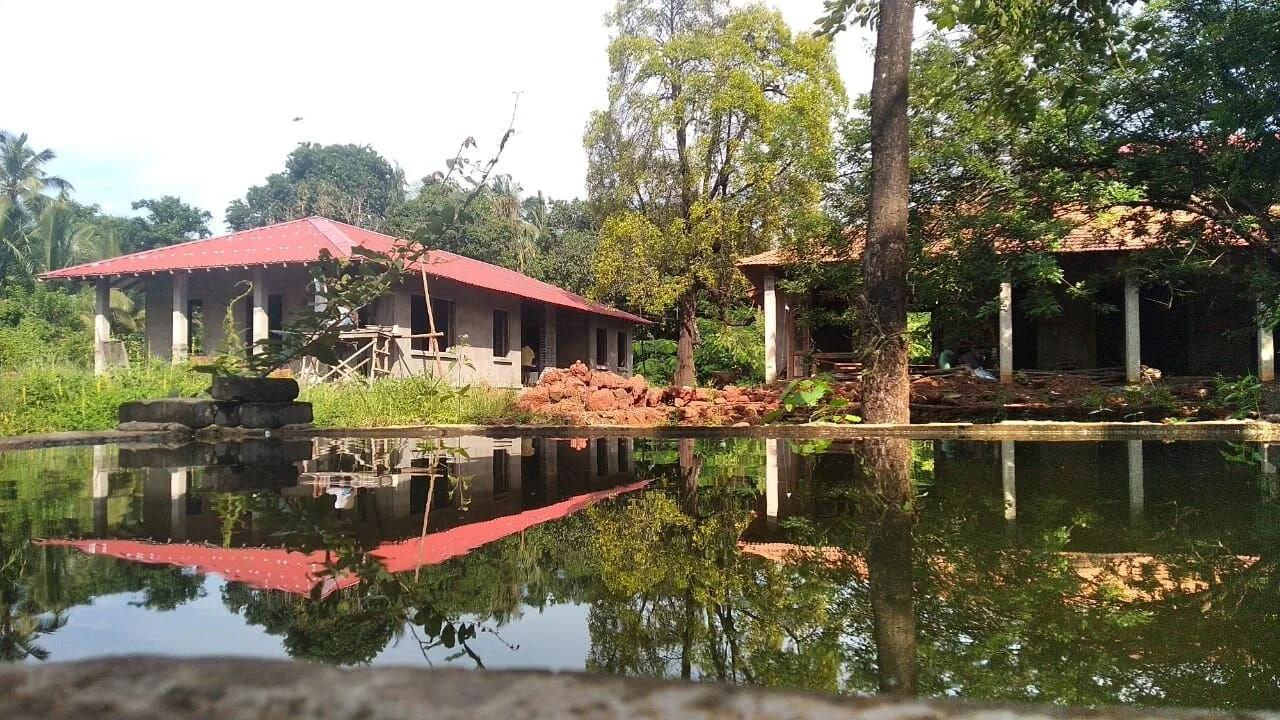
The project also prioritises the enhancement of the site’s resources and biodiversity through a comprehensive water-management system which includes a natural seasonal pond connected to a newly planned system of bioswales. This on-site wetland feature harvests rainwater, recharges depleted underground aquifers, and offsets the load on the public drain system. Furthermore, it preserves the pre-existing site habitat. It is a win to see that insects, birds, and animals continue to find the site a safe space even as they come in close contact with the human life around, making this truly a space for all seasons and species.