This article was written by me for World Environment Day and published on realty magazine website.
It feels like we are at war. At war with a virus that has caught the world off-guard. It spreads through air and we don’t have a cure for it, yet. We all recognize that this event will be life-changing and hope that the world can emerge from this only slightly bruised but overall resilient with a strong sense of solidarity, love and respect for humanity. While all our energies are focused on this crisis, there is a bigger elephant in the room where humanity has been on a war footing for some time now, that of climate change as a result of human activities.
The past few years have seen unprecedented wild fires, droughts and storm cycles around the world. A report by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation predicts that by 2050, there will be more plastic in the oceans than fish. In 2019, Okjokull became the first glacier in Iceland to disappear as a result of climate change. About 3.8 million hectares of primary rainforest was lost in 2019 alone. As per a report by Global Forest Watch, every 6 seconds, an area equivalent to the size of a football pitch of primary rainforest was destroyed in 2019. Entire islands have disappeared due to the rising sea levels in our oceans.
In March this year, while the world took a pause in an effort to contain COVID-19, we experienced and enjoyed cleaner air and cleaner waters- a definitive sign that humans are responsible for the environmental degradation that surrounds us. We have managed to pollute our glorious planet with poisonous gases and non-biodegradable waste, perhaps beyond repair. The silver lining is the speed with which the environment bounced back even with a temporary and short suspension of human activity. Pinning my hope on that, I wish that humankind can possibly mend our ways in an effort to bequeath a beautiful planet to our future generations.
Architects are generally taught to believe that they have the power to change the world for the better. We do this through design and also through advocacy. So even while we, as consultants, would recommend best practices, the conversion of ideas to real impact was marginal.
Many a times, Green Certification gets a bad reputation as it is a standardized platform of measuring sustainability across various cultures and geographies. The certification process forces us to keep detailed accounts, and make accurate calculations such that our sustainable efforts are not only in name but are real with measurable impact.
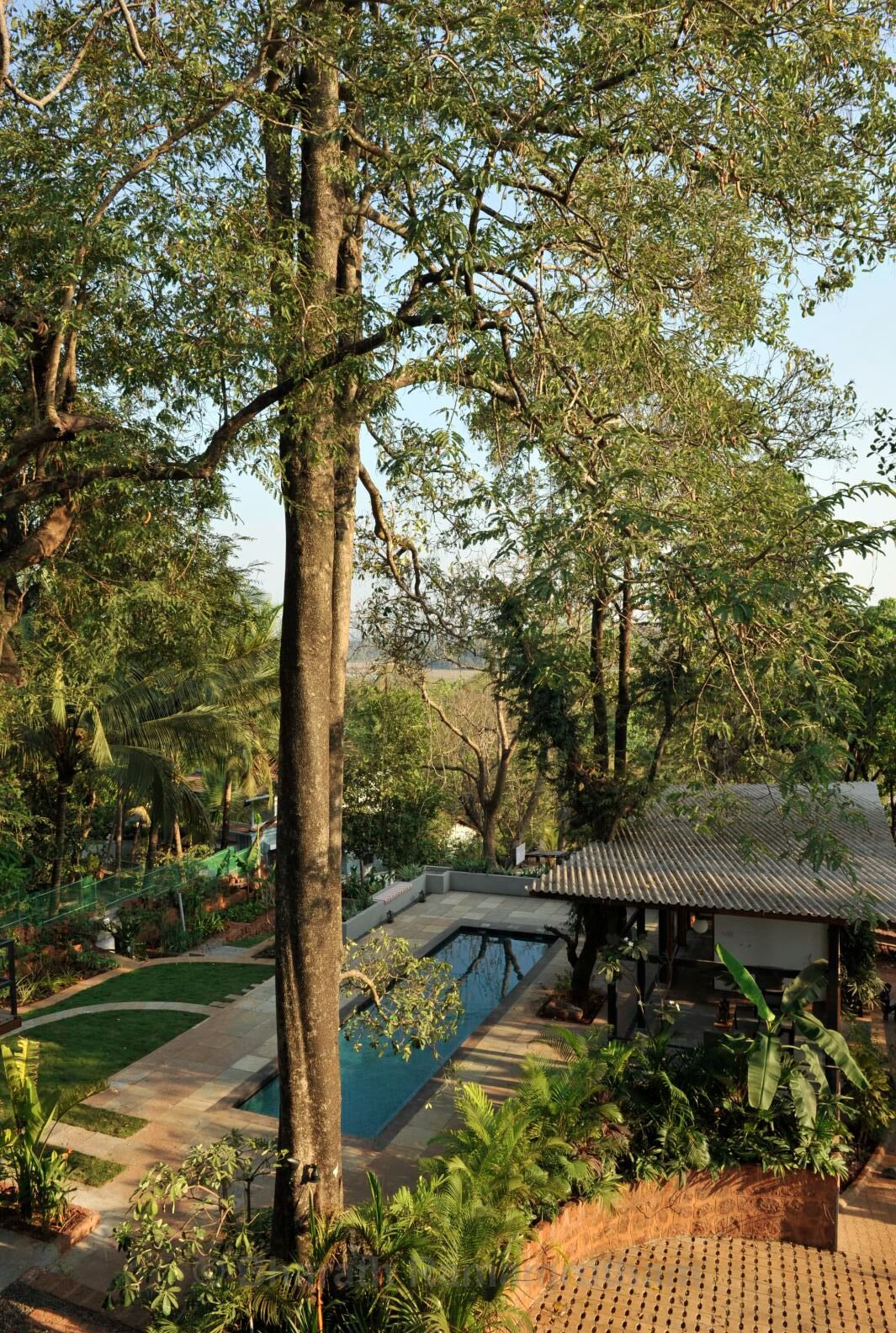
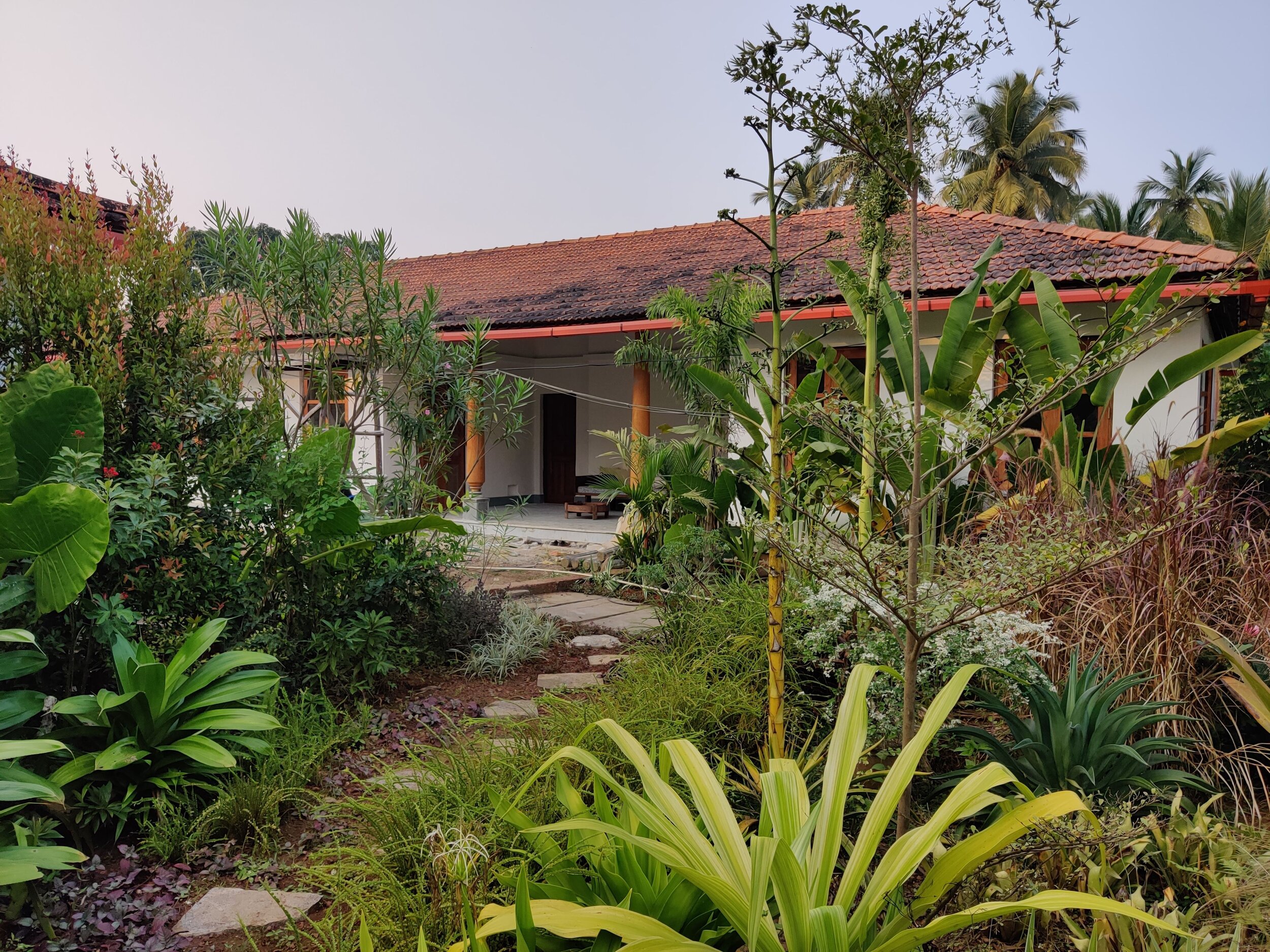
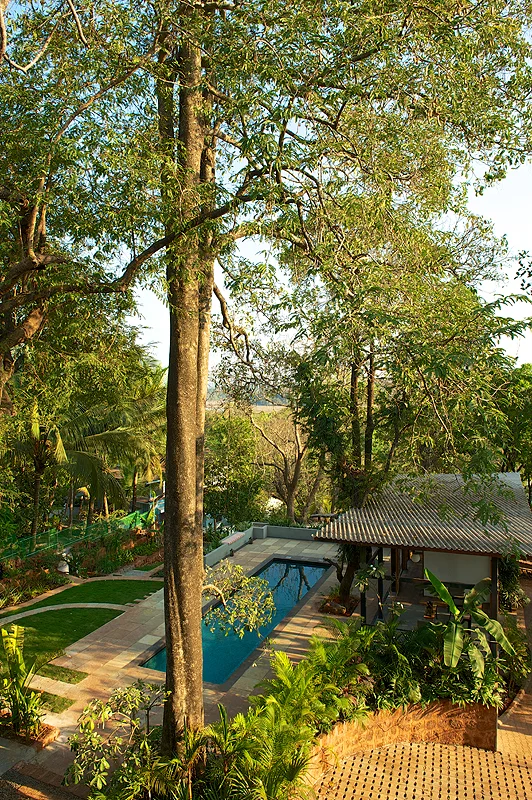
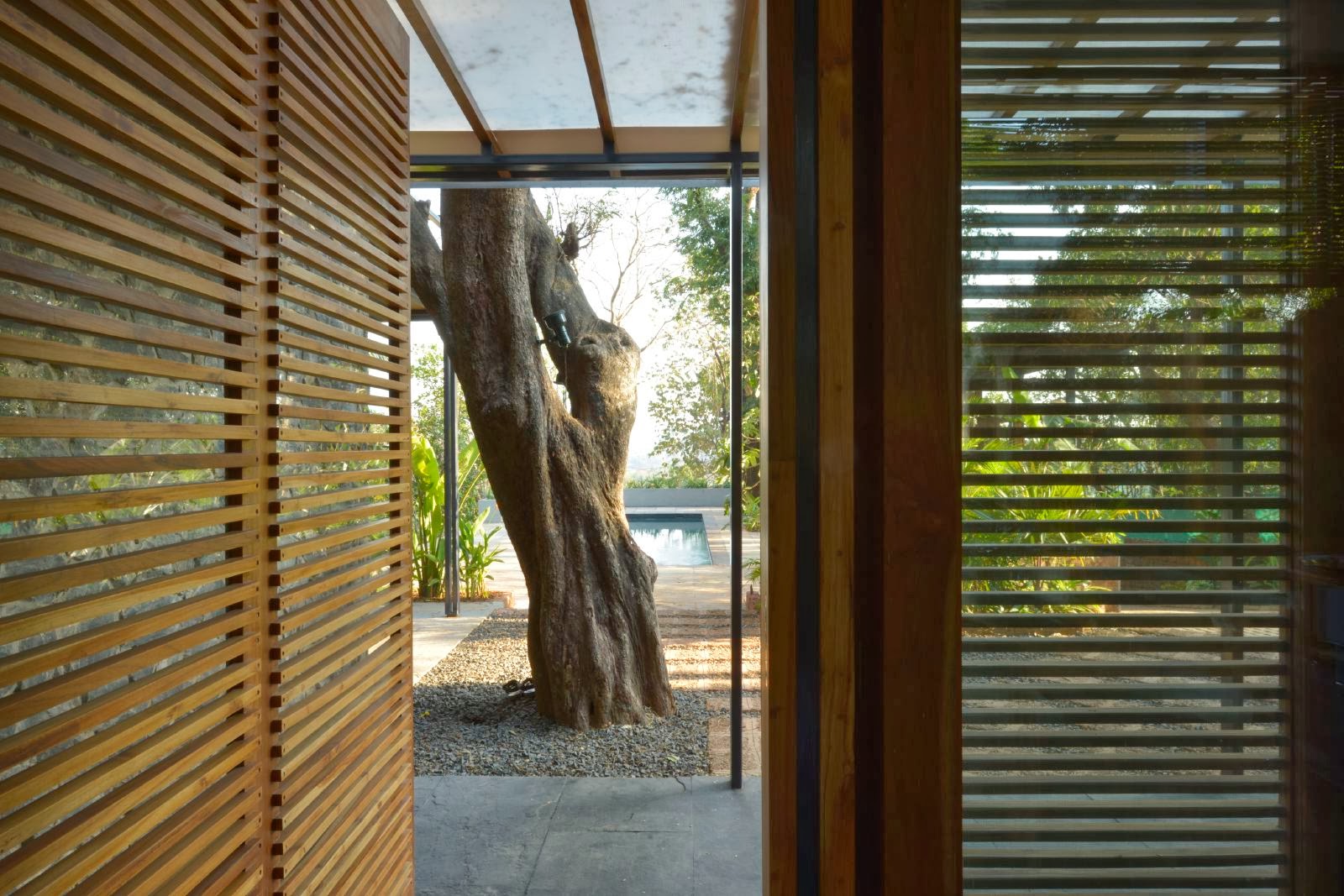
That said, certification is usually the starting point for us in our journey into sustainability. I firmly believe that ‘sustainability is common sense’. In architecture, it involves following sound design principles, respecting the land while planning new buildings and responding to the local climate and conditions.
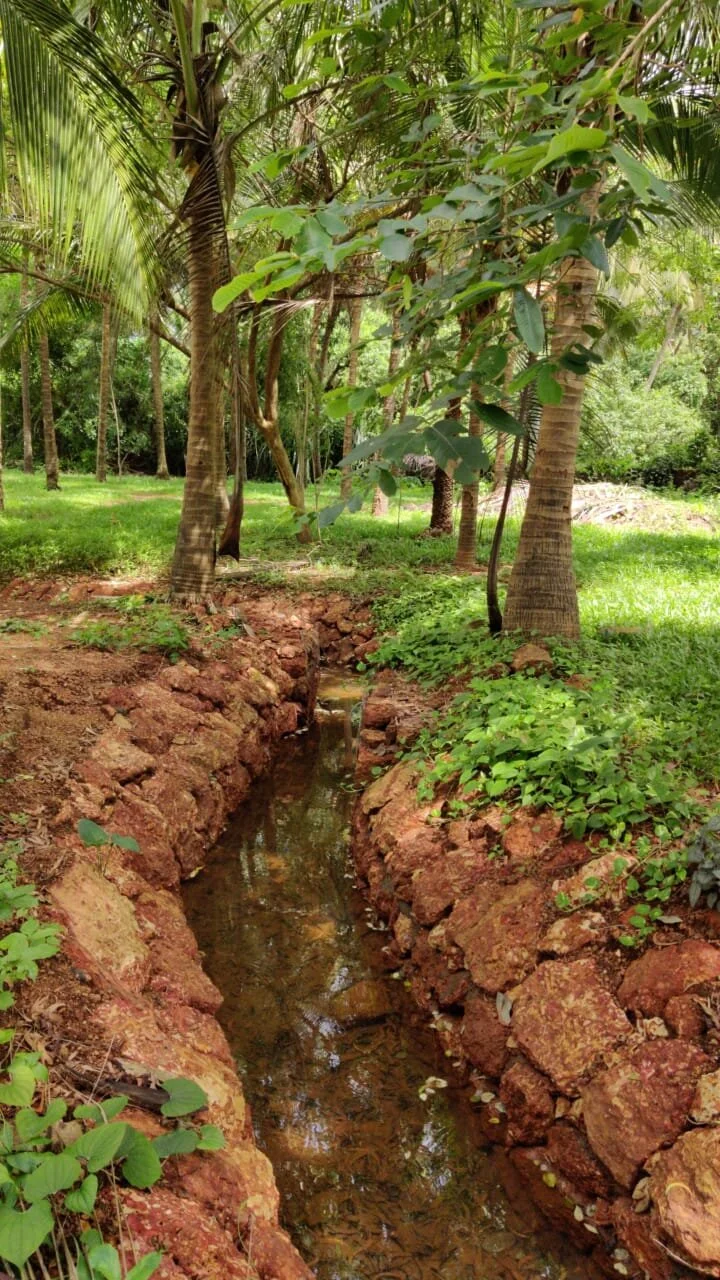
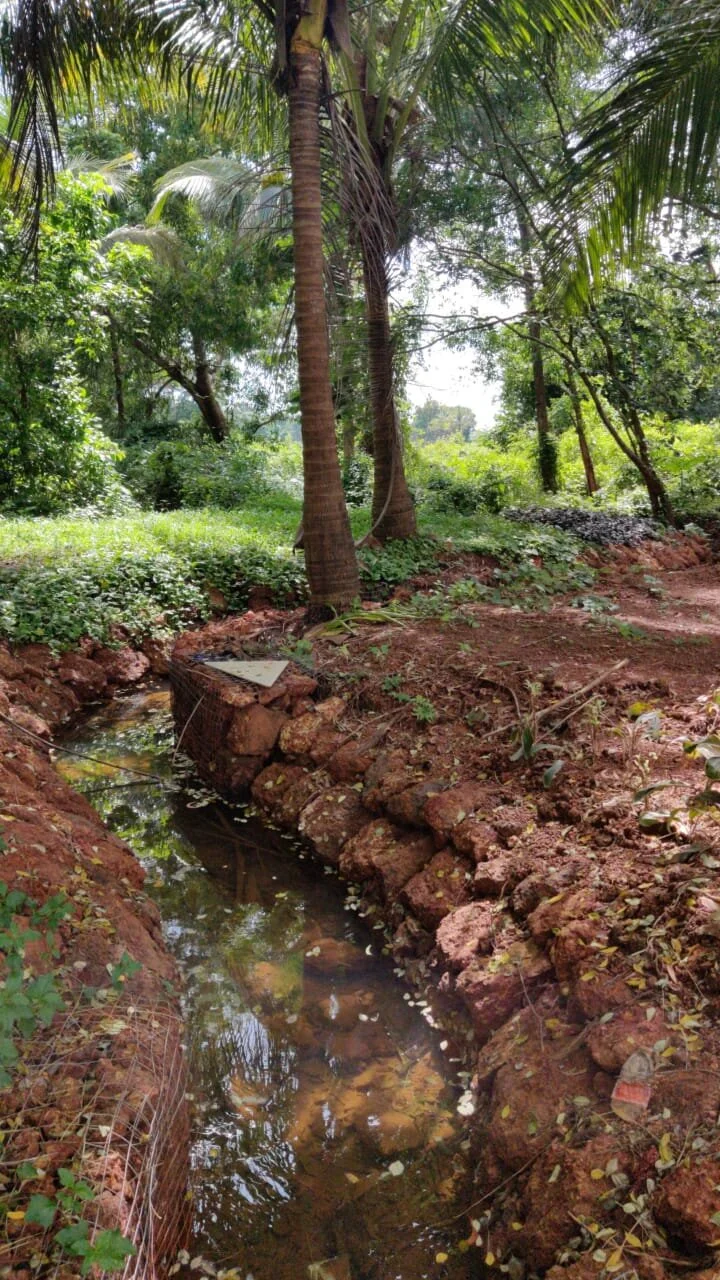
To pursue sustainability, we must try to conserve the natural resources within our own site (through rain water harvesting, renewable energy use and grey water recycling), use materials and employ design ideas that keep the building interiors cool or warm (and reduce the use of air-conditioning and heating), allow for ample daylight (to reduce the energy use for lighting during the day), use half flushes in bathrooms along with aerators to reduce the water flow in bath and kitchen fittings (to reduce water-use), maximize the use of materials that are produced locally, and use materials with a high recycled content.
These strategies for me are the low-hanging fruit that are easy to achieve with minimal cost escalation in the process. I also think that it is key to understand the lifespan of materials (regardless of their green features). If they have to be replaced in a short period of time, then they fail the test of sustainability. Finally, to achieve actual impact, we have to think about sustainability at every stage and factor it in every decision during the design and construction process.
To make sustainability a norm, the industry and consumer outlook also must change. We have found that most industry and product vendors still lack awareness on the importance of sustainability and green features in their products. Our perceived association that virgin materials are of superior quality, and reused materials are inferior, needs to change.
Government policy has sadly not been able to keep up with industry efforts and consumer desire for sustainable development. In Goa, when we started our practice in 2010, there was a subsidy for using solar water heaters. That subsidy is now being re-evaluated and not available to users. The policy of net-metering has stayed as a draft and has not been implemented. This makes the use of solar panels for power production not economically feasible for users.
While we endeavor to pursue sustainability as a hallmark in our projects, it is a struggle to achieve cost efficiencies. This process would be easier if we could avail of some government subsidies and programs. I believe that will attract a larger section of the industry to follow the path of sustainability.
As consumers, we should also look for ways to reduce our impact on the environment. Every small step makes a difference. We must remember that simple things can make a big difference. Climate change is a cause where the entire community must come together and play their part. The COVID crisis has evoked a sense of solidarity amongst us to fight a common enemy, I hope we can continue to utilize this positive spirit to fight climate change as well.